The introduction of the Electronic Health Records (EHR) Mandate changed the face of healthcare operations. If you're running any kind of healthcare organization, you know that providing simple, secure, and transparent access to patient data is essential. More than ever, data sharing is key to offering high-quality patient care.
Still, many organizations face challenges with EHR usability, interoperability, and data exchange. Bloated and legacy IT systems and the high overheads of maintaining in-house servers and infrastructure have made it difficult for companies to get the benefits of streamlined and reliable EHR services.
If you’re in this situation, cloud-based solutions offer a way forward. They may even be the only way for you to keep up with industry regulations and the shift to AI and ML-enhanced imagery, diagnosis, and reporting — not to mention tougher market competition. Despite the challenges involved, healthcare is finally waking up to the cloud, and the market for healthcare cloud computing software is growing at a healthy 23% CAGR.
This article looks at the impact cloud software deployment has on the efficiency of your healthcare operations. We list the benefits it offers, the hurdles to overcome during the transition, and the best practices for doing so. We’ll also discuss how cloud-based software will impact healthcare in the future.
The Benefits of Cloud-Based Solutions in Healthcare

Industry research shows that the most common challenges faced by today’s healthcare providers are staff burnout, tightened budgets, patient safety, and quality of care. While cloud deployment can’t solve staff shortages (with 34% of nurses close to quitting their jobs), it can reduce employee stress, cut expenses, and help improve healthcare outcomes. Here’s how.
Increased patient data accessibility
The core idea of EHRs is that all patient data is stored securely but can be easily accessed at any time. To meet these demands, systems need to
- Ensure 99.9% uptime
- Support access control rights monitoring
- Support API calls from third-party applications
- Implement strict user authentication in line with HIPAA requirements
Cloud service providers (CSPs) such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS are high-standard solutions that support all these features out of the box.
Faster clinical analyses and patient care
Looking up the results of previous blood tests online through an EHR is much faster than requesting them from another healthcare provider. Getting results automatically whenever a patient is admitted to another hospital is even better. But this requires configuring specific webhooks and API calls to act when certain conditions are met.
All cloud-based software has built-in tools for building workflows and monitoring and managing API requests. These tools automate and streamline data lookup so doctors can access required patient information faster. What’s more, having clinical test results from different facilities centralized in one EHR speeds up diagnosis and improves patient care outcomes.
Automated data processing and scalability
Processing new incoming data is naturally more resource-intensive than data storage and retrieval. Your infrastructure should be able to cope with your highest data processing loads at any time.
But running your IT infrastructure at full capacity 24/7 is not cost-efficient. Instead, it’s much better to activate the required solution, process the incoming batch of data, and then shut down instances to conserve your resources.
Cloud platforms let you scale your resources up and down based on a schedule, triggers, or manual settings. With a pay-as-you-go model, you pay only for the resources you use (as opposed to idle instances), and you can easily adapt to changing requirements.
Lower maintenance and staffing costs
In complex in-house IT systems, components can (and often do) fail in complex in-house IT systems. The cost of failover replacements and constant monitoring by skilled IT staff builds up over time. Cloud transition significantly lowers the costs of running your healthcare IT infrastructure in two main ways:
- Instead of keeping a team of highly-trained (and costly) system admins on standby, you can rely on support from your cloud provider in case of an emergency. This cuts the cost of resolving mission-critical incidents, which is especially relevant for smaller organizations.
- As your resources move to the cloud, you no longer have to maintain on-premise hardware and software licenses — a major IT expense for larger healthcare facilities.
Reduced risk of data loss
All cloud platforms support manual or automated backups. As this data is stored in the cloud, cloud backups don’t increase your OPEX like on-premise backups. In addition, with cloud services like DevOps, data backup and recovery are faster and more reliable, as you can scale resources up and down as needed and automate workflows.
By now, you may be wondering where the catch is. If everything is so great in the cloud, why aren’t all healthcare providers there yet?
The answer is — it’s hard to get it right the first time.
Challenges and Concerns of Cloud-Based Solutions in Healthcare
Shifting data and workflows to the cloud is hard work in any industry. Cloud-based platforms have different architectures from on-prem ones, and choosing and setting up the right solution requires expertise.
But it doesn’t stop there. Cloud deployment in healthcare presents an additional set of challenges, even if Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS provide HIPAA-compliant building blocks to get you started.
Data privacy and security risks
Cloud service providers have extensive features for identity and access management (IAM) and security. These need to be configured correctly to ensure that only authorized users and applications can access your patient and company data in the cloud.
This is non-trivial, as a key HIPAA requirement is that the PII of a country’s residents should not leave the country’s borders. Therefore, you must configure cloud backups and data access for your systems to ensure that patient data stays within specified locations.
Integration with existing systems
Your existing software ecosystem uses particular data formats, API integrations, and workflows to store and process medical data. Not all of these will match perfectly with cloud solutions for healthcare. This means you might need to replace some components.
This is not necessarily a bad thing. Your on-prem software toolkit was built at a certain time, under certain limitations, and in certain conditions, forcing it to work in a particular way. This might not be the most efficient way, or the one that will allow it to keep up with new trends.
When planning your transition to the cloud, you can address these flaws and build a more streamlined, performant, and cost-efficient infrastructure. However, this will take careful preparation and experience working with cloud solutions, which leads us to the next point.
A lack of in-house expertise
Few healthcare companies have a cloud infrastructure expert on their IT team, as the skill is irrelevant when you run your systems on-premise. But when you decide to move to a cloud healthcare platform, the need for such expertise becomes obvious.
It’s true that CSPs have in-depth manuals and guidelines on best practices for using their services, but mastering these takes time. You can also opt for paid migration support, but this can lead to undesirable vendor lock-in. The middle road solution is selecting a software services company with a proven record of successful cloud transitions.
Standards compliance
While CSPs have building blocks for ensuring compliance with regulations, connecting them correctly is your responsibility. This task becomes even more challenging once you decide to integrate new technology such as IoT, AI, and ML since moving data to the cloud involves transferring patients’ private details over a public cloud infrastructure.
Once again, this hurdle can be cleared, but you need help from competent cloud architect specialists.
Let’s now discuss what you can expect from new healthcare technology trends and look at how you can future-proof your cloud-based platforms for healthcare.
The Future of Cloud-Based Solutions in Healthcare
All large CSPs have services and features dedicated to handling AI algorithms, training ML models, and building IoT platforms. Choosing the features that will maximize value for your company is a key part of moving your workloads to the cloud.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Centralizing all medical data in the cloud opens the door to advanced data processing with AI and ML medical imagery tools. By analyzing patterns and markers in millions of anonymized medical images, AI & ML algorithms can learn to quickly filter out irrelevant details. This helps doctors and clinical researchers reach a correct diagnosis faster, thus improving patient care outcomes.
Internet of Things
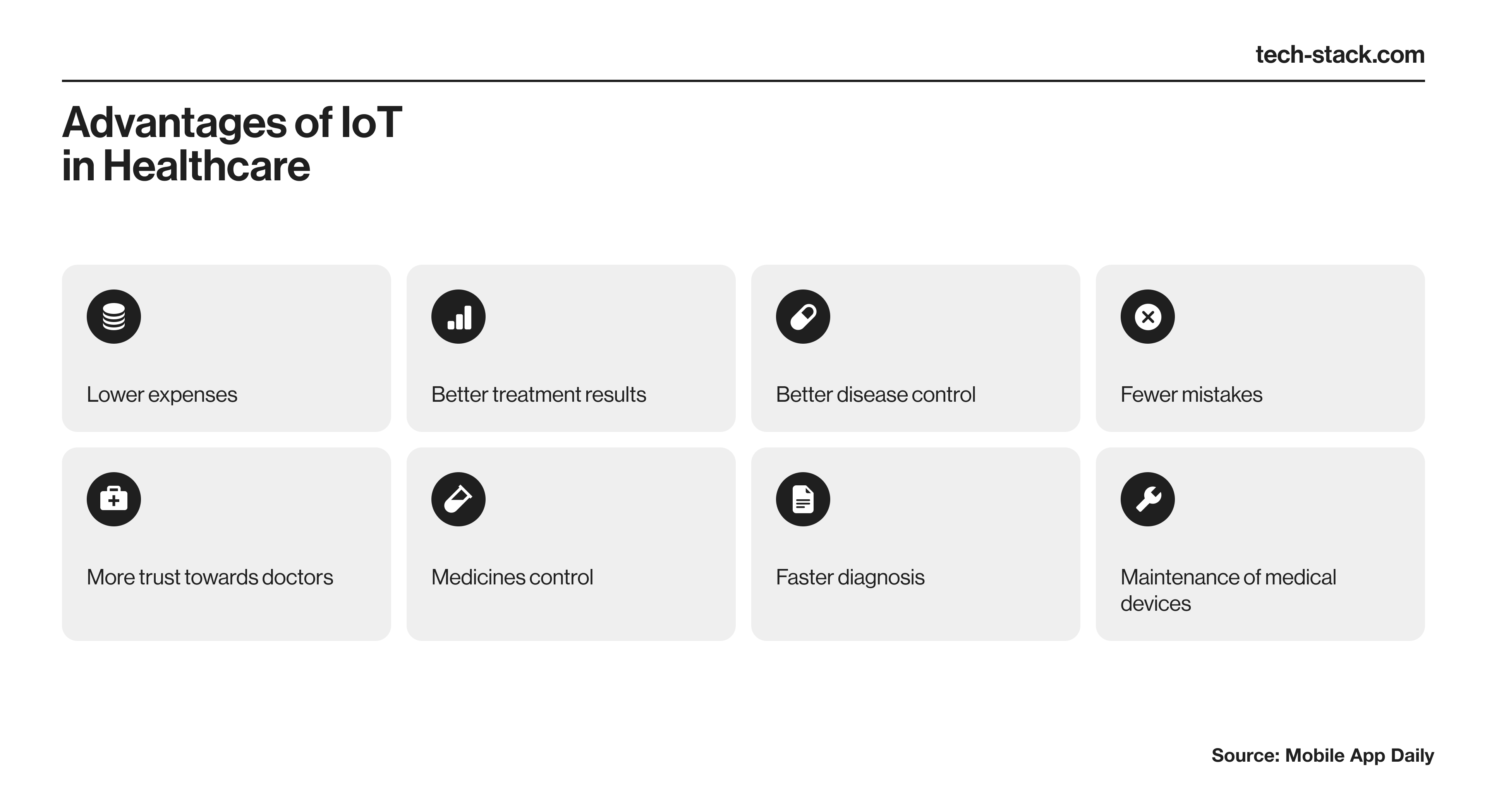
Wearable sensors in hospital units, smartwatches, bands, and other wearables monitoring patient conditions at home generate a huge amount of data for use in telemedicine.
Yet the sheer volume, velocity, and variety of information gathered by IoT sensors make the cost of deploying such systems on-premise prohibitively high. Cloud software for healthcare provides a more affordable and efficient solution, with sufficient resources for turning a flood of data into actionable insights for clinicians.
Cloud-native applications
Building healthcare software to be cloud-native addresses many challenges of successful cloud migration. It also gives you full access to the benefits of cloud-based features and services. As a result, cloud-native solutions for healthcare look set to rise.
As always, there’s a catch. By definition, cloud-native deployment prohibits using on-prem data storage (or makes such architectures excessively complex and costly), and some medical institutions still have data protection policies requiring them to store PII on-site.
But as the general trend toward cloud transition to conserve limited resources gains pace, even the most conservative healthcare providers will have to adapt or risk losing their competitive edge.
Conclusion
Cloud-based platforms for healthcare offer many tangible benefits:
- Reduced operating costs and higher systems reliability, thanks to minimal on-premise IT infrastructure and less support staff
- Easier implementation of telemedicine, training AI and ML algorithms, processing of IoMT data, and remote consultations, thanks to centralized cloud-based patient data storage
- Better support for patient self-care and self-assessment, remote patient monitoring and alerts, resulting in stronger preventive care and cost savings
However, moving an existing healthcare IT ecosystem to the cloud requires in-depth knowledge of cloud-based platforms, including platform architecture, configuration, integration, and ongoing maintenance. There are also other things to consider before migrating to the cloud.
This is where Techstack comes in.
Our team has experience with designing, implementing, configuring, and maintaining cloud infrastructure for partners, including healthcare providers. We can help create a cloud-based system that will help allocate your resources cost-efficiently and keep you ready to integrate AI and IoT innovations.
Contact us to discuss how Techstack can help you maximize the efficiency of your healthcare operations and patient care!






